Background
The study aimed to evaluate the potential of Momordica cymbalaria Fenzl (MC) in healing burn wounds. Partial-thickness scald wounds were induced on SD rats by pouring hot molten wax at 800°C on the dorsal area of the rat. Rats were placed into five groups (n=6). 1st group served as the wound control (Untreated) group. The rest of the 4 groups received SSC (1% w/w), 5% extract of MC, Scaffold, and 5%, Saponin of MC topically respectively twice daily for 14 days. Wound contraction and period of epithelization were checked on days 1,9 and 14. On the 9th day, the granulation tissue was isolated and estimated for hydroxyproline content and antioxidant enzymes. A part of the granulation tissue was processed for histopathology studies.
Results
5% extract and Saponin of Momordica cymbalaria Fenzl promoted wound contraction and decreased the period of epithelization when compared with control but lesser than the SSC-treated group. It also enhanced collagen synthesis and wound stability, as demonstrated by an elevation in hydroxyproline content. The histological examinations also affirmed the healing potential of the drug, which showed a full form of epidermis layer, less inflammatory cells, more no. of collagen fibers, and blood vessels lesser than the SSC-treated group and scaffold. Endogenous enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidant levels increased significantly in the Momordica cymbalaria Fenzl -treated groups, while lipid peroxide levels decreased.
Conclusion
By 5% extract, Momordica cymbalaria saponin, and scaffold have great healing capacity in burn wounds and have a beneficial influence on the various stages of wound restoration.
Aim
A Scientometric study examines the publication’s quantitative and qualitative trends in a particular research area during the year 2023.
Materials and Methods
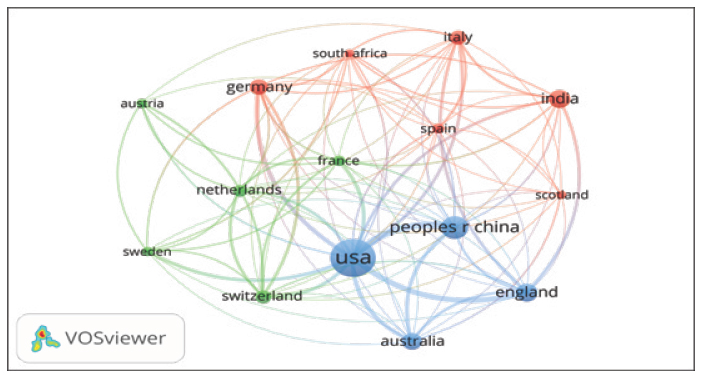
The present study investigates 333 ChatGPT research outputs of world published 2023, indexed in the Web of Science Core Collection database software, including bibliometric Biblioshiny and VOSviewer, have been used for data Analysis. Further, we have analysed the top 15 authors, institutions, countries and journals were analysed with the various bibliometric indicators.
Results
Annals of Biomedical Engineering journal has the highest number of publications 8.982% in the world. Duke University, USA has the maximum number of publications 1.80%, The authors who registered the highest number of publications were Anonymous, He YB And Wu HY (USA), most productive publisher were identified from Springer Nature published 20.606% publications.
Conclusion
This study suggests that the number of publications on ChatGPT have remained stable over the year and maximum research emerged from the development countries. The quality of the study is entirely depending on the input information imported from the Web of Science (WoS) database.
Background
Cardiac surgeries are medical emergencies to prevent life threatening incidents or mortality. However, due to postoperative complications, there is discussion over subjecting high-risk individuals to cardiac surgeries. Drop of morbidity and Higher survival rates of the cardiac surgery can be good predictors of the outcome of surgery. Proper life style modification and adherence to medications avoids secondary cardiac risk factors.
Objectives
Objective was to analyze the health-related quality of life and medication adherence in post-operative cardiac surgery patients.
Materials and Methods
This was a hospital based prospective cross-sectional study carried out over 6 months. SF-36 questionnaire and MMAS-4 were used to evaluate the HRQoL and medication adherence respectively. Mann Whitney U test, mean and standard deviation statistical tools were used to analyze the data.
Results
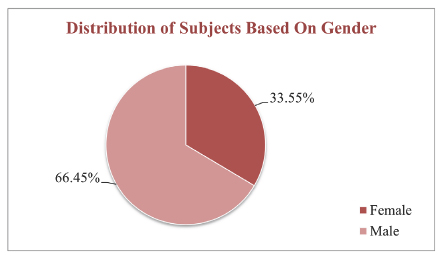
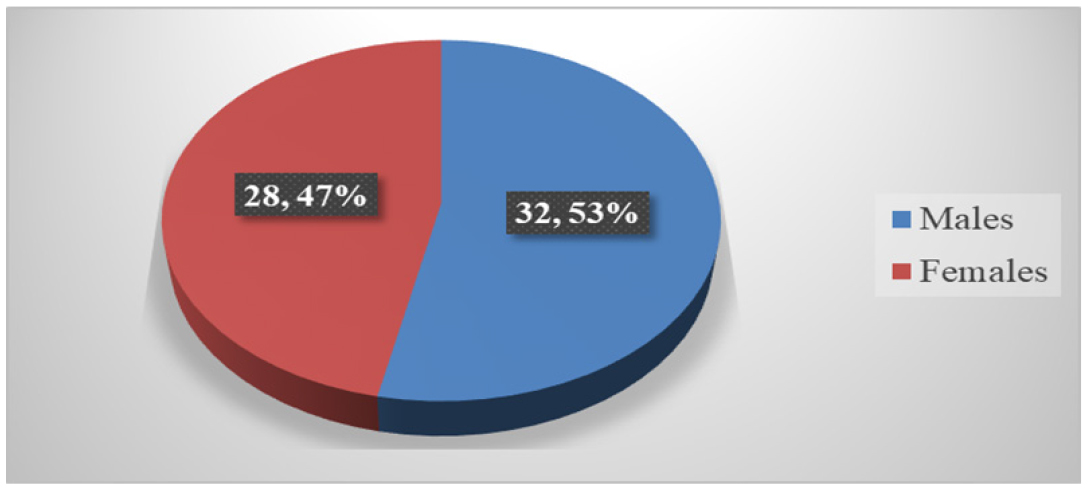
A total of 152 patients were enrolled in the study of which majority of patients undergone CABG. HTN was found to be most common comorbidity followed by diabetes. The study found that the HRQoL in post-operative cardiac surgery patient was significantly low, which was observed in role limitation due to emotional problems (28.41). Females had better quality of life scores (p value <0.00001). High adherence was seen in 32.24% patients while 28.29% patients had low adherence.
Conclusion
Assessing medication adherence with HRQoL, high adherent patients had good QoL. Majority of patients had moderate adherence. The overall study showed that there was less impact in QoL in post-operative cardiac surgery patient. So, in order to improve QoL, health care experts must plan interventions accordingly.

Introduction
Urolithiasis is a hard deposit of minerals and salts that form inside the kidney, ureter, and bladder in the urinary system. Kidney stones are a common disease of the urinary tract. Prevention of stones mainly depends on the mechanisms of the stone formation, daily water intake, and food habits.
Aim and Objectives
A prospective observational study was conducted on risk factors, and prescription patterns in urolithiasis patients.
Materials and Methods
The study was conducted from August 2022 to February 2023 in Khammam, Telangana. Men and women were included as a sample of subjects aged 18-60 years. The total number of samples was 200.
Results
Urolithiasis was more commonly observed in males than females aged 18-60. Urolithiasis developed in individuals who consumed less water, frequently ate non-veg, and had a family history of calculi. Out of 200 patients, only 27 patients had complications like AKI, and abdominal pain and painful incomplete urination was the most reported symptoms.
Conclusion
The prevalence, risk factors, and prescription pattern of urolithiasis were observed in this study. The Formation of Kidney stones may be due to diet, age progression, gender, obesity, genetics, and lifestyle factors. A better understanding of the epidemiology of urolithiasis is further essential to plan effective treatment and preventive strategies.
Background
The use of the evidence-based clinical practice recommendations, offer guide on efficient and prompt therapy of Coronary Artery Disorders (CAD), is inconsistent, especially in developing nations. A wide range of pharmacological classes were needed to treat CAD. In economically developed countries, effective methods for their utilisation, diagnosis, assessment, and management are well-defined; nevertheless, in poor countries, they have not yet been fully embraced. Present study aims to study the various categories of the drugs prescribed to the Myocardial Infarction (MI) patients at a tertiary care hospital.
Materials and Methods
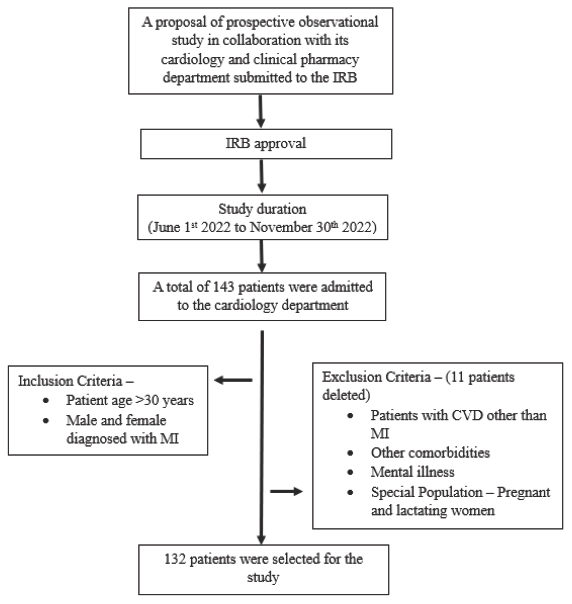
We studied trends in drug prescription patterns among 132 eligible patients diagnosed with MI in the current prospective observational study, which was carried out in a teaching hospital with tertiary care facility.
Results
The results of the study represented, male patients over the age of 40 were more likely to have MI. According to a section of the myocardium affected by an infarction, Anterior Wall Myocardial Infarctions (AWMI) account for 60% of all cases, followed by Inferior Wall Myocardial Infarctions (36%) (IWMI).
Conclusion
The most often recommended medications were hypolipidemics, followed by anticoagulants and antiplatelets.
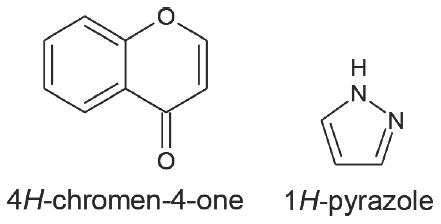
Background
The pyrazole nucleus has a five-membered heterocycle with two nitrogen atoms next to one another. The two nitrogen atoms are near in pyrazole nucleus heterocyclic compounds. Chromones are benzoannelated -pyrone-ringed heterocyclic compounds having a single oxygen ring. 4H-chromen-4-one
Materials and Methods
All Chromones and Pyrazole derivatives were synthesized by conventional reflux method. 1-(4-chloro-2-h ydroxy-5-methylphenyl)ethanone, penta fluoro benzoic acid, 2, 3, 4, 5-Tetrafluorobenzoic acid, Pyridine, Hydrazine Hydrate, Guanidine Hydrochloride, Ethanol, Con. Hydrochloric acid and Phosphorus oxychloride i.e. POCl3 were used for the synthesis of Chromones and Pyrazole
Results
Compared to Ciprofloxacin and Gentamycin, the anti-bacterial results for the substances or their derivatives like 7-chloro-6-methyl-2-(pentafluorophenyl )-4H-chromen-4-one (CC); 5-chloro-4-methyl-2-[5-(pentafluorophenyl)-1 H-pyrazol-3-yl] phenol (CD); 5-chloro-2-[2-imino-6-(pentafluorophenyl)-1,2-dihydropyrimidin-4-yl]-4-m ethylphenol (CE); 1-(4-chloro-2-hydroxy-5-methylphenyl)-3-(2,3,4,6-tetrafluorophenyl) propane-1,3-dione (CG); 7-chloro-6-methyl-2-(2,3,4,6-tetrafluorophenyl)-4H-chromen-4-one (CH); 5-chloro-4-methyl-2-[5-(2,3,4,6-tetrafluorophenyl)-1H-pyrazol-3-yl]phenol(CI); 5-chloro-2- [2-imino-6-(2,3,4,6-tetrafluorophenyl)-1,2-dihydropyrimidin-4-yl]-4-methylphenol (CJ) against S. aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Moreover, the compounds code name like 2-acetyl- 5-chloro-4-methylphenyl pentafluorobenzoate (CA); 1-(4-chloro-2-hydroxy-5-methylphenyl)- 3-(pentafluorophenyl) propane-1,3-dione: (CB); 2-acetyl-5-chloro-4-methylphenyl 2,3,4,6-tetrafluorobenzoate (CF); 1-(4-chloro-2-hydroxy-5-methylphenyl)-3-(2,3,4,6- tetrafluorophenyl)propane-1,3-dione (CG) a derivatives gives potent anti-bacterial activity against Escherichiacoli.
Conclusion
The title compounds’ and its derivatives’ in vitro antibacterial activity against a few human pathogenic pathogens were investigated. Gram-positive Gram-negative Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli, along with Staphylococcus aureus, are the bacteria. Studies on the link between structure and activity have shown that compounds containing chromones and derivatives of the pyrazole had higher activity than those containing electron-donating groups.
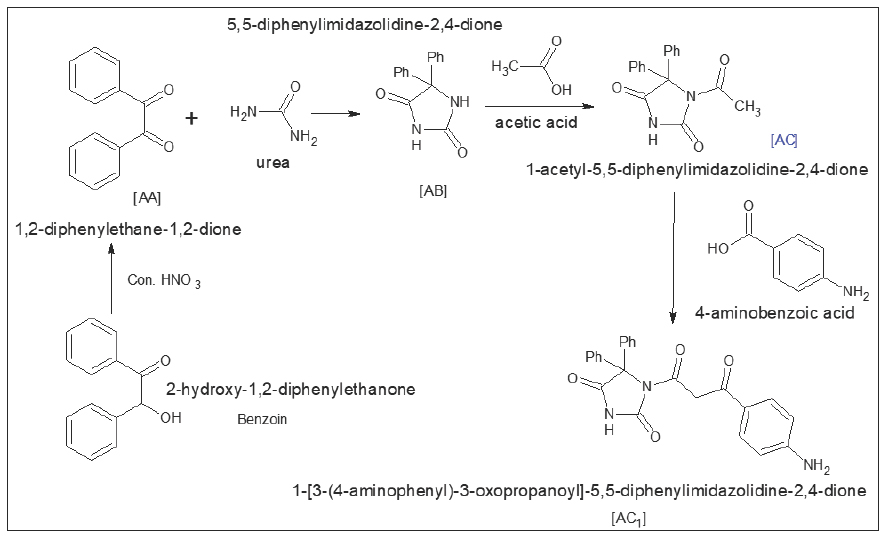
Background
A heterocyclic hydrocarbon with distinct fundamental structural features in its molecular structure of 5, 5-diphenylimidazolidine heterocyclic ring. It is an imidazolidine and aromatic dibenzene fused ring. The flexible heterocyclic compounds that contain two atoms of nitrogen in 5, 5-diphenylimidazolidine. 5, 5-diphenylimidazolidine ring and its derivatives have a robust and promising biological action. In this study, we create a number of 1-[3-(4-ami nophenyl)-3-oxopropanoyl] derivatives. A compound with anticonvulsant properties is -5, 5-diphenylimidazolidine-2,4-dione (AC1). The Strychnine Induced Convulsion Method was used to test the pharmacological samples for anticonvulsant action. The compound 5,5-diphenylimidazolidine-2,4-dione was synthesized together with its 14 total derivatives.
Materials and Methods
Benzoin; Benzil; Urea; Glacial Acetic Acid; 4-amino benzoic acid; Con. HNO3; Formic Acid; 2-Nitro Aniline; 4-Nitro Aniline; Aniline; Acetyl Chloride; Formic Acid; 4- amino Phenol are used for the synthesis. IR, NMR and MS are used for interpretation.
Results
Our research led us to the conclusion that a variety of compounds have strong anti-convulsant properties. The compound 5,5-diphenylimidazolidine-2,4-dione (AB); 1-acetyl-5,5-diphenylimidazolidine-2,4-dione (AC); 1-[3-(4-hydroxy-2-[2-oxo-4 (phenylamino) ethyl]butanedioicacid)-3-oxopropanoyl]-5,5-diphenylimidazolidine-2,4-dione (AC5); 1- [3-(4-oxo-4-(oxo(4-phenylamino)-3-oxopropanoyl]-5,5-diphenylimidazolidine-2,4-dione (AC6); 1-[3-(4-(phenyl amino)benzoic acid) -3-oxopropanoyl]-5,5-diphenylimidazolidine-2,4-dione (AC7) gives strong anti-convulsant effects against phenytoin drug.
Conclusion
The title compounds and its derivatives were examined for their ability to treat convulsion. Studies of the relationship between structure and activity revealed that compounds containing 5, 5-diphenylimidazolidine derivatives that have an electron-withdrawing group have higher activity than those that have an electron-donating group.

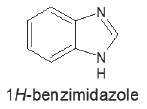
Background
Epilepsy was described as utmost common be habitual brain complaint. A typical symptom of epilepsy is unbridled storms due to transient neuronal discharges. Despite the fact that numerous novel anti-convulsants have been developed in the Indian request but after treatment of new and current curatives; certain kinds of seizures are still not sufficiently controlled by smaller side goods.
Materials and Methods
The exploration reported on concentrated work on molecular docking and ADME of the relations that do between the chlorinated benzimidazole derivations and the sodium (Nav) voltage-gated channels. A series of the benzimidazole derivations were planned and studied in silico was performed by through a sodium channel inhibitor GABAergic pathway. The medicine- likeness parcels of the designed composites were prognosticated.
Results
All the designed composites showed good in silico ADME and molecular docking parcels and delved for Voltage-gated Sodium Channel (NavMs)-5HVX inhibitory exertion. According to molecular docking studies, all composites showed better commerce with target protein and could be the potent asset of sodium channels via a GABAergic pathway. The designed benzimidazole derivations analogues may be more effective anticonvulsant drugs that are also safer.
Conclusion
Voltage-gated Sodium Channel (NavMs)-5HVX is one of the crucial enzymes of GABAergic pathway biosynthesis in different natural fiefdoms and is set up in beast and also in humans. Voltage-gated Sodium Channel (NavMs)-5HVX proteins belong to the class of superfamily. It’s the most conserved protein. Unlike other enzymes, Voltage-gated Sodium Channel (NavMs)-5HVX also gives strong particularity.
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
The objective of the in silico study was to evaluate GRIN2B gene using bioinformatics tools so as to discover the probable effect of mutations of this gene as well as its protein-protein interactions with the pathobiology of depression.
Materials and Methods:
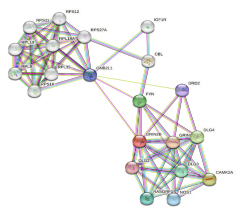
In silico analysis of SNPs of GRIN2B gene was conducted using its accession IDs and their FASTA amino acid sequences obtained from NCBI. SIFT, Polyphen-2, CADD score, MetaLR and mutation assessor were the bioinformatics softwares utilized for the study. Protein–protein interaction was assessed by string database.
Results:
Analysis of SNPs of GRIN2B gene by SIFT revealed 56.42% mutations were tolerated and 43.58% were damaging. Polyphen-2 analysis showed 46.36% SNPs were deleterious and 53.64% were benign mutations. On metaLR analysis, 7.93% of the SNPs found to be dangerous mutations whereas 92.07% of them were tolerated. CADD scores presented 2.67% damaging and 97.32% tolerant mutations of GRIN2B gene. A total of 2.46%, 39.72%, 27.3% and 30.51% of the mutations were found to be high, low, medium and neutral as per the mutation assessor tool. According to a string database analysis, there were 11 nodes, 37 edges (instead of the expected 14 edges), an average node degree of 6.73, and an average local clustering coefficient of 0.79 and protein protein interaction enrichment p-value was 1.018e-07.
Conclusion:
The results propose that GRIN2B gene mutations that are deleterious and its interactions as obtained by the bioinformatics softwares may have a crucial role the pathogenesis of depression.
ABSTRACT
Background:
Natural products emerged as potential lead molecules in the drug discovery paradigm. During COVID-19 pandemic, researchers explored several natural agents with antiviral activity. The objective of the present study is to predict inhibitors of important COVID-19 targets from a set of potential candidates belonging to natural origin using molecular docking and dynamic simulation.
Materials and Methods:
Important target, main protease (Mpro) (PDB ID: 6M03) was selected for this purpose. Twenty natural agents were selected for molecular docking (Auto Dock vina 4.2). Molecular dynamic studies were performed using GROMACS.
Results and Discussion:
Among the selected natural products, tetrandrine, an isoquinoline alkaloid (-8.9 kcal/mol), and etoposide, a podophyllotoxin (-8.4kcal/mol) showed excellent binding affinity compared to remdesivir (-7.1kcal/mol) with Mpro. Further, the stability of the complex formed between Mpro and tetrandrine was confirmed in molecular dynamic studies at 100ns.
Conclusion:
The present in silico investigation could lead to the development of tetrandrine as a potent COVID-19 inhibitor.
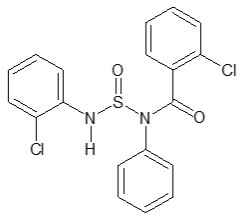
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
This study describes a new route to the synthesis of novel (2-chloro-N- {[(2-chlorophenyl) amino] sulfinyl}-N -phenylbenzamide derivatives. Benzamide-based derivatives were prepared through a reaction of benzoyl chloride with 2-chloroaniline with conventional methods by alkylation with Thionyl chloride and then a reaction with 2-chloroaniline to get target compound i.e., novel 2-chloro-N-{[(2-chlorophenyl)amino]sulfinyl}-N-phenylbenzamide. Benzamides are structural parent of carbonic acid amide of the benzoic acid. Benzamides has the carbon snippet being attached to oxygen and also a nitrogen group attached with hydrogen atom
Objectives:
To synthesize 2-chloro-N-{[(2-chlorophenyl)amino]sulfinyl}-N-phenylbenzamide derivative and with its Characterization and its biological activity.
Materials and Methods:
The structure confirmations were done by FTIR, Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (MRS) and MS. The (2-chloro-N-{[(2-chlorophenyl) amino] sulfinyl}-N-phenylbenzamide compounds and its derivatives were investigated for in vitro screening. Structural activity relationship studies reveal that compounds possessing an electron-withdrawing group exhibit better activity than electron-donating groups.
Results:
Based on the results obtained, when compared to common medicines like Ciprofloxacin; the compounds 2-({[(2-chlorobenzoyl)(phenyl) amino]sulfinyl}amino)phenyl formate (BB8), 2-({[(2-chlorobenzoyl) (phenyl) amino] sulfinyl} amino)phenyl-2-aminophenyl-2-(4-nitrophenoxy) aniline (BB9), 2-({[(2-chlorobenzoyl) (phenyl) amino]sulfinyl}amino)phenyl-2-aminophenyl-2-(3-nitrophenoxy) aniline (BB10) showed good significant activity. Against S. aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Conclusion:
The title compounds and its derivatives were investigated for anti-bacterial Activity. Structural activity relationship studies told that electron-withdrawing group exhibit good activity than the electron-donating groups.
ABSTRACT
Background:
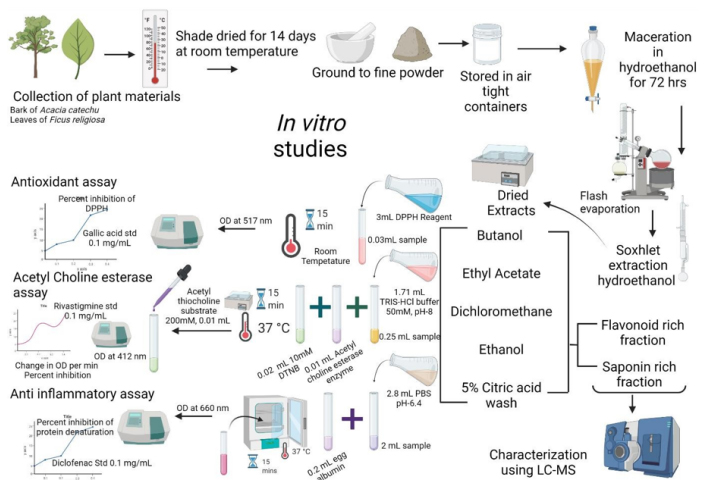
Neuroprotection is a process of recovery and salvage of the nervous system, function, and structure of cells. Several modulators are leading to neuronal damage and cell death, causing many neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, Huntington’s, etc. Conventional medicinal therapies like Donepezil and Rivastigmine have a wide range of long-term effects. Acacia catechu and Ficus religiosa are two popularly known plants in herbal medicine. Their primary use is in the treatment of various inflammatory diseases. The present study investigates the beneficial effect of these plants in neuroprotection by in vitro and silico methods.
Materials and Methods:
We determined aqueous extracts of both A. catechu and F. religiosa for their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and acetylcholinesterase activities. The extracts were subjected to Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectroscopy (LC-MS) analysis. In addition, molecular docking was performed for the inhibitory activity of the five selected ligand components identified from LC-MS analysis against two well-known neuroreceptors [1b41(Acetylcholinesterase) and 2V5Z (Human monoamine oxidase b1)] by AutoDock tools v 1.5.6. 2.7.3. These results and standards Donepezil and selegiline were compared for their binding energy, inhibition constant, and intermolecular energy.
Results:
Both A. catechu and F. religiosa have shown moderate to high neuroprotective activities in vitro and in silico.
Conclusion:
The A. catechu and F. religiosa extracts possess remarkable antioxidant, anti-inflammatory potential with potent neuroprotective components. Further studies on combining these two plants into a formulation could benefit neuro-restoration and prevent neuroinflammatory processes.
ABSTRACT
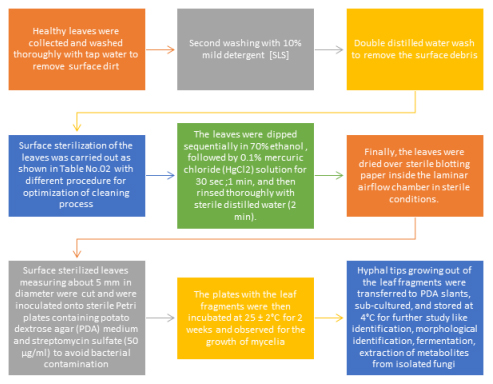
Phyllanthus acidus (L.), a medicinal plant, shows numerous pharmacological properties like antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, hypoglycemic effects, neuroprotective, anti-diarrheal, anti-pyretic, and analgesic and anaesthetic effects which may be attributed to the bioactive compounds produced by Phyllanthusacidus or due to associated endophytic fungi. In the current work, Phyllanthus acidus L. leaf samples were analysed for the presence of endophytic fungi and to produce quercetin, a beneficial chemical, from them using an optimal surface sterilising process and analytical techniques., five fungal endophytes were isolated and they were preliminarily identified by morphology. According to morphological features of isolated endophytes identified as Aspergillus sp. Aff and Chaetomium sp. Aff. Interestingly, only leaves were used to isolate all five fungus, and in response to selected plant samples, the overall colonisation frequency from surface sterilised leaves was found to be 7.5%. Shake flask culture approach used for fermentation followed by extraction and purification process. Analytical and thin-layer chromatography, HPLC of ethyl acetate extract of isolated fungal endophytes PAEF3 showed a distinct phytochemical fingerprinting profile.The fact that quercetin, a key component of Phyllanthusacidus L., is used for a variety of properties like Antiviral, Anticancer, and Antidiabetes, makes this study of practical significance as well.

ABSTRACT
Background:
The present study has been carried out to explore antifungal property of folklore medicinal herbs Solanum trilobatum, Spathodea campanulata, Syzygium jambos and Tylophora indica prevalent among the tribal communal in the Western Ghats of Coimbatore district.
Materials and Methods:
The aqueous and organic leaf extracts obtained by cold maceration method was confirmed for its antifungal activity against Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus fumigatus by agar plate dilution method.
Results:
The methanolic extracts of S. trilobatum, S. jambos and T indica exhibited substantial (p<0.001) fungal growth inhibition against A. flavus with IC50values 40.63, 94.56 and 84.52 μg/mL respectively. The ethanolic extracts of S. trilobatum, S. campanulata, S. jambos and T indica also revealed (p<0.01) inhibitory activity against A. flavus with IC50 values ranging between 102.34-146.79 μg/mL, whereas the S. campanulata methanolic and chloroform fractions of S. jambos influenced mycelial inhibition against A. flavus with a IC50 values at 147.92 and 111.08 μg/mL respectively. Furthermore, the methanolic extracts of S. campanulata exposed highly significant antifungal activity against A. fumigatus, (p<0.001) with IC50 value at 95.3 μg/mL. Analogous antifungal significances were also observed among methanolic extracts of S. jambos and T. indica against A. fumigatus with IC50 values at 131.52 and 114.51 μg/mL respectively. The other extracts were not up to the pronounceable level of fungal growth control against the two fungal strains used in the assay.
Conclusion:
The alcoholic leaf extracts of selected plants were more active against tested fungal strains when compared to the chloroform and aqueous extracts. Further surveys and findings have to be fixed to recognize the antifungal metabolites present in the chosen herbs.
ABSTRACT
Aim:
To identify native plant species with high tolerance and remediation potential for specific pollutants present in the industrial area, aiming to develop effective and sustainable phytoremediation strategies for environmental cleanup.
Materials and Methods:
The study conducted field investigations around an industrial area to screen plants for heavy metal accumulation. Soil and plant samples were analyzed for heavy metals using the acid extraction method, and five plant species were identified, with I. globosa showing potential for metal accumulation.
Results:
The soils around the industrial area of Mangalore, Karnataka, were severely contaminated with heavy metals. This contamination had a significant impact on the plants growing in the area. Among the identified plant species, I. globosa from the Poaceae family demonstrated the potential for accumulating and translocating heavy metals. The study confirmed the efficacy of plants growing around industrial areas in absorbing and accumulating heavy metals, indicating their potential for phytoremediation applications.
ABSTRACT
Background
As many pharmaceuticals are removed via the kidneys, a dose adjustment for some medications is necessary in individuals with decreased renal function to prevent toxicity. This study aimed to modify the dose in individuals with renal failure using creatinine clearance as a screening tool.
Materials and Methods
From November 2021 to April 2022, prospective observation research was carried out in a government hospital’s Department of general medicine. The study includes all patients diagnosed with renal illness above the age of 30, patients with elevated serum creatinine levels, and renal patients with concomitant diseases. From the patients’ medical records, information on the serum creatinine level, age, sex, and prescribed medications and their dosages were gathered. The Cockcroft-Gault (CG) equation was used to get the predicted creatinine clearance. The benchmark for dose adjustment was the American College of Physicians Guideline for Drug Prescribing in Renal Failure.
Results
In this study, 100 patients were screened, and among them, 60 were found to be CKD patients. 512 drugs were prescribed in 60 patients, of which 505 were appropriately adjusted and 2 drugs were inappropriately adjusted in 7 (11.6%) patients and 53 (83.3) patients were appropriately adjusted. Patients with renal impairment have a median age of 50-60 years (56), a serum creatinine value of 2.4, and an estimated CCR value of 126.8. Comorbidities are present in 45 (or 75%) 60 patients.
Conclusion
According to the findings, patients with renal impairment admitted to the hospital frequently made dosing errors. In patients with renal impairment, improving the quality of drug prescriptions may enhance the quality of care overall.

ABSTRACT
Background
The brain is highly susceptible to Aluminium’s (Al) toxic impact due to its elevated lipid content and oxygen utilization but, relatively scanty levels of antioxidants. Al is known for its strong pro-oxidant activity. Hence oxidative stress in the brain is a likely outcome of Al toxicity. Previous studies report sensory, motor and cognitive deficits in animals exposed to various Al compounds. Hence, this study was undertaken to find how dose, and time span of aluminium exposure influence the pro-oxidant activity and antioxidant handling capacity in female Wistar rats’ cerebellum and hippocampus.
Materials and Methods
Two groups of female Wistar rats were given four different aluminium chloride oral doses of 0, 50, 100, 200 mg/Kg body weight daily for a time span of four and eight weeks. Oxidative level was assessed by estimating GSH, LPO, SOD, Catalase, GPx and GR in cerebellum and hippocampus of rat brain. Data was analysed by 2-way ANOVA and Bonferroni ‘t’ test was used for multiple group comparisons.
Results
Al exposure in female rats resulted in increased lipid peroxidation, while antioxidants GSH, SOD, catalase, GPx and GR were depleted in cerebellum and hippocampus. However, these changes were predominantly significant only in aluminium doses of 100 and 200 mg/Kg in both 4 and 8weeks studies. But, GPx in the cerebellum and catalase in hippocampus showed a crucial reduction even at 50 mg/Kg dose on eight-week exposure.
Conclusion
Aluminium has enhanced the synthesis of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) in rat cerebellum and hippocampus, as noted by the increase in lipid peroxidation which was not balanced by the elevated synthesis of antioxidants. In addition, aluminium at higher doses of 100mg/Kg dose and more had a significant negative impact on the antioxidant protective system. Therefore, it is vital to minimize our aluminium exposure from different sources in our everyday lives.

ABSTRACT
Introduction
The reported hypocalcemia was low in denosumab-treated postmenopausal women with osteoporosis (0.05-1.7% to 7.4%). The major prediction factors were Vitamin D and calcium levels and renal function.
Aim
To assess the rate of hypocalcemia in patients with osteoporosis treated with denosumab, with normal renal function and Vitamin D.
Materials and Methods
A retrospective analysis was conducted using the medical records (2021-2022). We looked for hypocalcemia (albumin-adjusted calcium lower than 2.1 mmol/L).
Results
We included 201 women with postmenopausal osteoporosis who received denosumab treatment plus prophylactic Vitamin D3 capsules. The mean age of the patient population was 75.7 ± 7.0 years (56-91 years). Hypocalcemia was observed in 46 (23%) patients following a single subcutaneous dose of denosumab 60 mg. Median calcium was 2.25 mmol/L (minimum: 0.890 mmol/L, maximum: 2.6 mmol/L). Fourteen (30.4%) patients had severe cases (< 1.8 mmol/L) and required parenteral correction. A comparison between hypocalcemia and patients with normal calcium indicated that the strongest predictors of hypocalcemia were pretreatment parathyroid hormone levels (9.9 ± 0.5 vs. 7.6 ± 0.5 pg/L, respectively; p<0.005). Eight patients (3.3%) developed hypophosphatemia. The baseline serum albumin, calcium, and alkaline phosphatase levels were normal.
Conclusion
The denosumab-associated hypocalcemia is more prevalent than previously shown in patients with osteoporosis receiving adequate calcium and Vitamin D supplementation. An elevated parathyroid hormone is an important predicting factor in patients with normal calcium and Vitamin D levels.
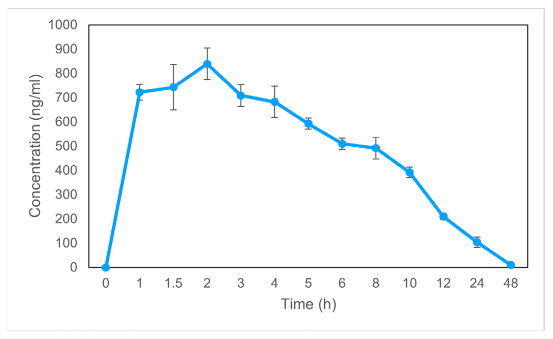
The study’s objective was to evaluate Exenatide for treating Type 2 Diabetic Mellitus (T2DM) in an animal model. The safety profile and dose determination for the in vivo antidiabetic study were established through an acute toxicity study conducted by OECD guideline 425. The plasma levels of exenatide were studied using a pharmacokinetic model in rats. After Exenatide were given to the rats, their behavior, biochemical, and hematological characteristics were tested. Animals were administered Streptozotocin (STZ, 60 mg/mL, i/p) to induce diabetes. Blood glucose levels above 250 mg/dL were diagnostic of diabetes in animals. The drug was non-toxic in toxicity investigation. Results showed that administration of drug did not cause any significant change in behavioral, biochemical, or hematological markers. It was revealed that Exenatide significantly lowered blood glucose levels in diabetic animals. The results of the study indicated that Exenatide has the potential to be utilized as an alternative antidiabetic medicine against Type 2 Diabetes.
Background
Pharmaceutical residues are biologically active in trace concentrations. This has increased worries about their potential hazards to human health and living organisms and has highlighted the need to treat them once they are discharged into aquatic ecosystems. In this study, the potential of removal of Ciprofloxacin antibiotic (CIP) using novel magnetic Activated carbon nanocomposite (Fe3O4/AC) was studied.
Materials and Methods
For conducting equilibrium analysis, a batch system was considered and operated under conditions including CIP initial concentration, solution pH, Fe3O4/AC dosage, and mixing time. Analyzing the experimental data was done using different isotherm and kinetic models.
Results
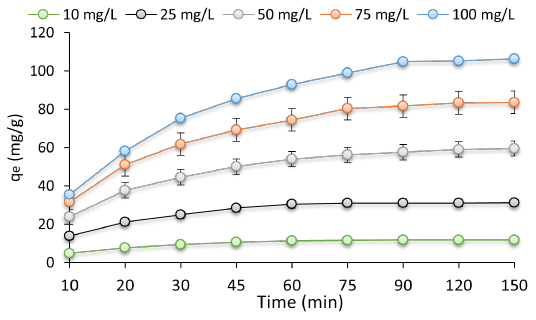
The analysis of the physical and chemical properties of Fe3O4/AC was indicative of the successful preparation of Fe3O4/AC; the surface area, microspores volume, and average pore diameter were observed to be 129.2 m2/g, 0.512 cm3/g, and 4.6 nm, respectively. A removal percentage of 100% was obtained for CIP using Fe3O4/AC under optimal values of the studied parameters; the optimum values of these parameters were as follows: solution pH of 5, adsorbent dosage of 0.8 g/L, and an initial CIP amount of 25 mg/L. The Langmuir model was found to be best for labeling the equilibrium data (maximum CIP adsorption capacity of 156.2 mg/g was obtained based on the Langmuir model). The fit of experimental data kinetic with the pseudo-second-order equation was also detected.
Conclusion
The obtained results let us suggest Fe3O4/AC nanocomposite as a decidedly competent adsorbent for removing CIP.

Background
Capecitabine (CAP), a BCS class-I drug which is used for the treatment of Colorectal Cancer (CRC). Site specific and enzyme activated drug delivery was achieved by albumin coated nanoparticles. Co-administration of Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPI) with the tablet dosage form of CAP lowers the dissolution of the CAP due to elevated gastric pH, resulting in decreased CAP absorption. To overcome this absorption, issue the albumin coated CAP NPs were administered through rectal route as suppositories dosage form.
Materials and Methods
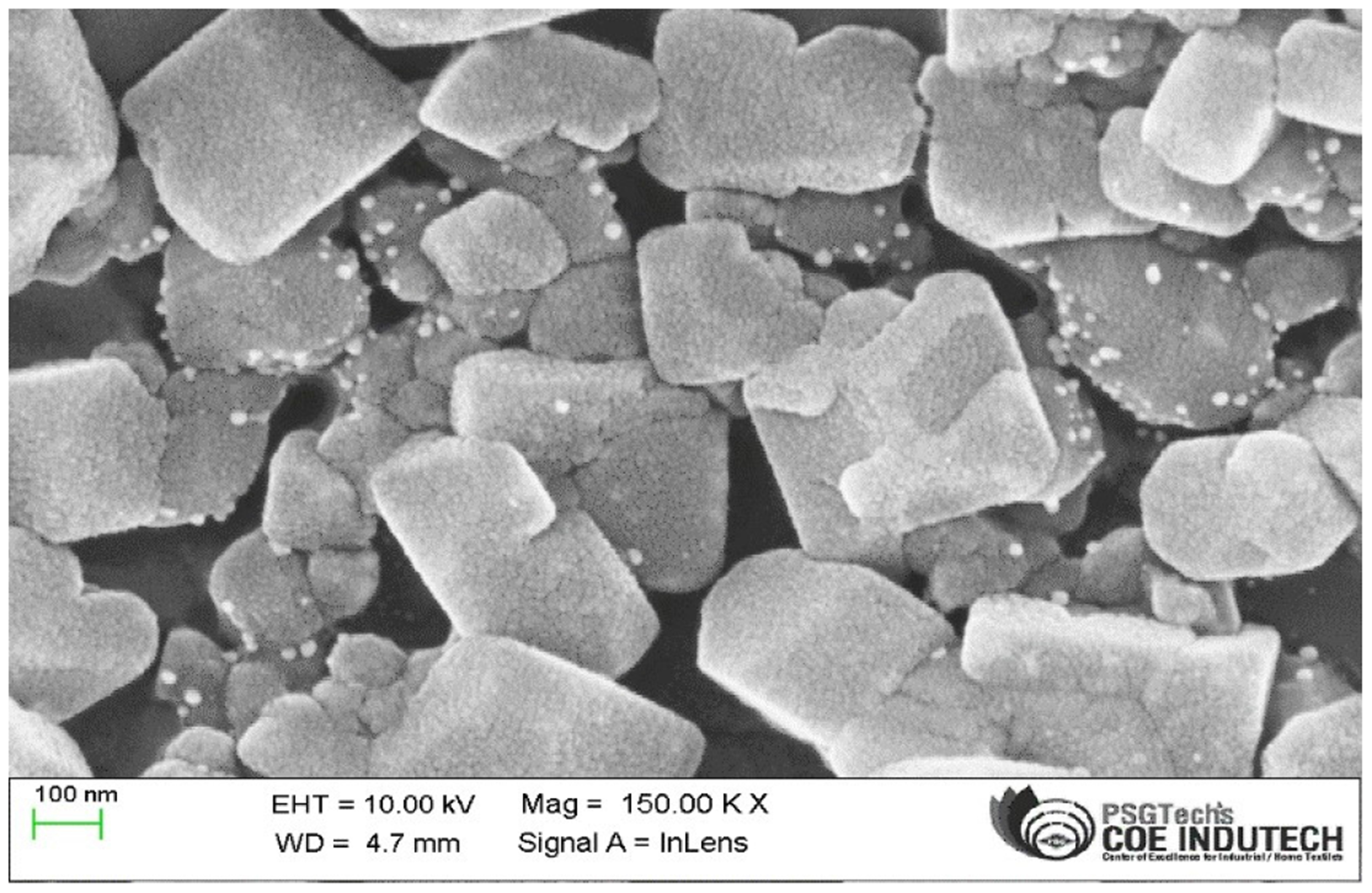
The capecitabine nanoparticles were prepared using different concentrations of Poly Lactic-co-Glycolic Acid (PLGA) polymer by salting-out technique and were characterized. Further, the optimized polymeric nanoparticles were coated with Egg Albumin (EA) using a glutaraldehyde cross-linker and characterized for their particle size, zeta potential, polydispersity index, drug content, SEM, and in vitro drug release. The suppositories were prepared by fusion moulding method using different grades of PEG as a base and evaluated for various parameters and in vitro drug release.
Results and Discussion
The particle size of the optimized CAP NPs and the EA coated CAP NPs were determined to be 171.7 nm and 239.6 nm respectively. The in vitro release of CAP from the EA coated NPs and the suppository formulation shows 88.3% and 81.0% respectively.
Conclusion
Capecitabine suppositories were formulated and the quality control parameters were assessed for the site specific and enzyme activated drug delivery in the management of colorectal cancer with help of literature references.
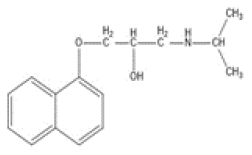
Background
To design and develop propranolol hydrochloride sustained-release tablet formulations using different grades of HPMC and MCC and their in vitro evaluations. The effect on drug release from tablets and other characteristics by various grades of polymers were studied and compared.
Materials and Methods
Propranolol hydrochloride, microcrystalline cellulose (PH-101), Microcrystalline Cellulose (PH-102), HPMC (K15 M), HPMC (K100 M), HPMC (K4 M), HPC LF, Isopropyl alcohol, Povidone (K-30), Magnesium Stearate were used in the different formulations. Direct compression, dry granulation and wet granulation methods were used for the preparation of tablets.
Results
Among different formulations, SR008 having HPMC K100M was showing better sustained release characteristics, 69.1%, 76.6%, 82.3% for 8, 10, 12 hr respectively compared to other formulations with 71% moisture content and 71N hardness.
Conclusion
The matrix embedding technique using HPMC K100M has successfully extended the release of propranolol hydrochloride. It is particularly suitable for obtaining directly compressed sustained-release matrix tablets with appropriate standards and well-reproducible drug release profiles. In contrast to thrice daily prescriptions of the conventional formulation, the designed formulations can be prescribed once daily dose leading to a reduction in dosing frequency and per-day drug dose. It is concluded that HPMC K100M in appropriate proportions is suitable for formulating sustained-release tablets which exhibit diffusion-controlled Higuchi kinetics for propranolol hydrochloride.
ABSTRACT
Introduction
SLNs have a surfactant-stabilized solid lipid core. They circumvent liquid lipid constraints and increase drug stability. Lipids promote oral medication absorption through the lymphatic pathway and replace hepatic first-pass metabolism. Using a 2-factor, 3-level, 32 full factorial design, the researchers optimized percentage Encapsulation Efficiency (%EE), drug content, and particle size to enhance the candesartan cilexetil-loaded SLN formulation.
Materials and Methods
The BCS class II low soluble Candesartan was used to formed as SLN and optimized utilizing independent variables Imwitor 900K and tween 60 concentrations and dependent factors %EE, drug content, and particle size. FTIR showed no drug-excipient interaction. Along with in vitro drug release.
Results
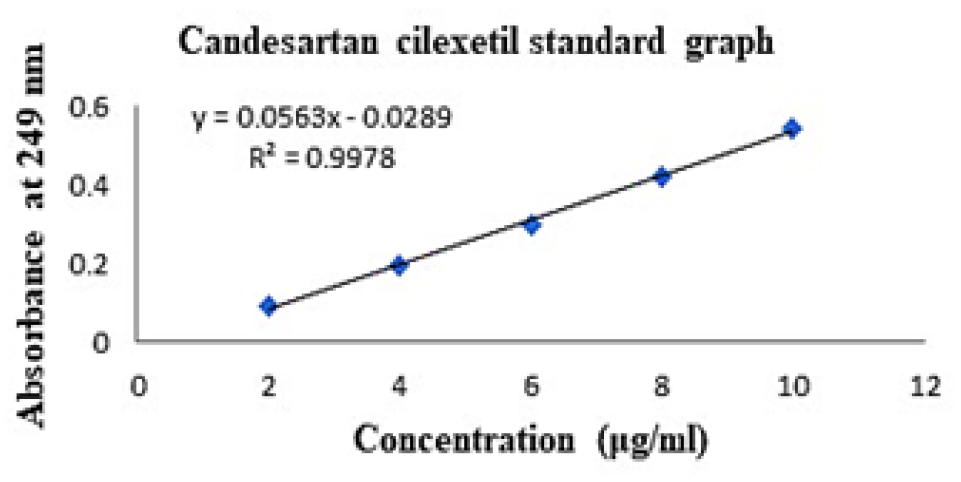
The optimized 13 formulations had %EE from 78.47 to 94.61, drug concentration from 57 to 107%, and particle size from 357 to 705 nm. SEM showed that certain particles were coagulated and near-spherical, supporting particle size and dispersion. C-SLN-7 released 60.39% and C-SLN-12 46.4% during 24 hr in vitro. BCS class II low soluble CC’s calibration curve was a straight line with an R2 value of 0.9978, indicating the drug’s standard curve. The improved SLN formulation may improve oral bioavailability of poorly soluble medicines.
Conclusion
The enhanced SLN formulation of candesartan cilexetil increased encapsulation efficiency, drug content, particle size, and in vitro drug release. Changes in lymphatic absorption may improve oral absorption of highly lipophilic medicines. The work sheds light on SLNs’ lipophilic drug delivery potential.
ABSTRACT
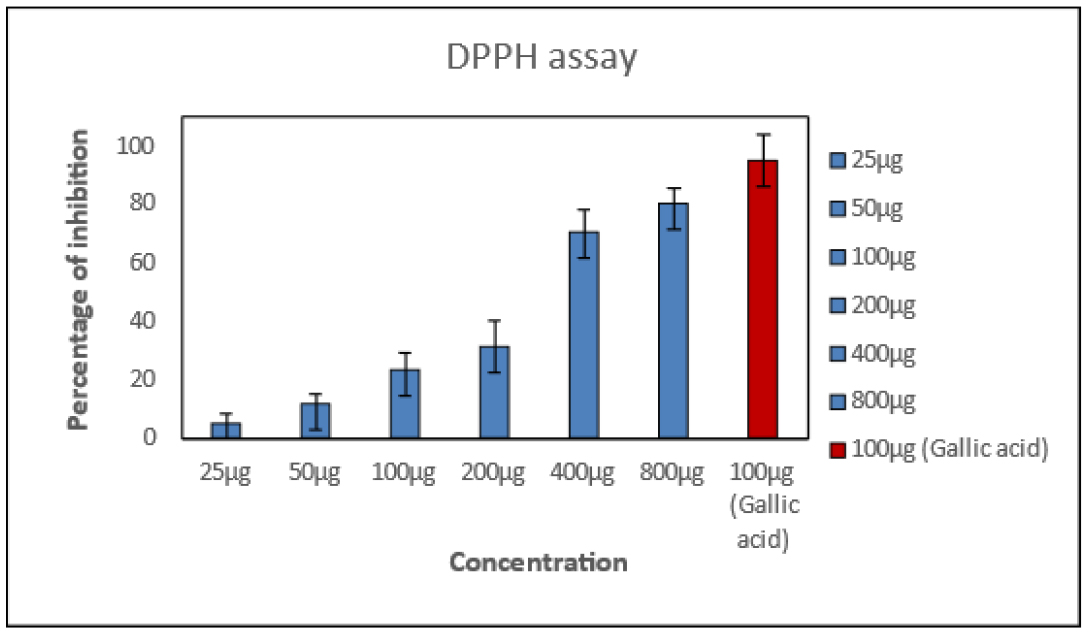
The objective of the present was to formulate a novel topical P-herbo dosage form by incorporating the extracts of Azadirachta indica, Centella asiatica, and Ocimum gratissum and compare the efficacy. There is a strong clinical need to establish an appropriate formulation with the possibility to treat Ance by once-a-day application. Topical P-herbo dosage forms were prepared using various concentrations of extracts, with other excipients, and were evaluated for physicochemical parameters such as Viscosity, pH, spreadability, and extrudability to determine the suitability of the topical formulation. Anti-oxidant activity by DPPH assay, anti-microbial assay against Cutibacterium acne, and in vitro skin irritation studies were also carried out. Studies revealed, in vitro skin irritation showed the least irritation score for formulations (Gels-0.2; cream and ointment- 0.3) compared to 1% clindamycin and positive control. On analyzing the results, the OF-2 formulation was found to be optimized, due to its good anti-microbial, antioxidant activity with high skin deposition of herbs extract. Further, the optimized formulation was subjected to stability studies in compliance with ICH guidelines for a period of six months and all evaluated parameters remained intact even after six months, thus confirming the stability of the formulation. Hence, the present research concludes that the ointment formulation containing P-herbo extract showed prolonged action and was an excellent substitute for synthetic antiacne formulations with once-daily application.

ABSTRACT
The highly infectious Corona Virus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) had spread and created a havoc worldwide due to lack of risk assessment and quick transmission. The outbreak created epicenters are still being reported daily. Different demographics, genetics, ethnicity, geography, ABO blood groups and HLA genotypes have significantly different rates of COVID-19 incidence, severity, and death. Because of this, finding a successful preventive approach has therefore been a primary focus, leading to the creation of large number of management strategies. In light of this, it had become essential globally, to develop COVID-19 vaccines, monoclonal antibodies and habitual activities like yoga, in order for everything to resume, as they had before the pandemic. Finally, it can now be observed the pre-pandemic normalcy. so, one should be prepared physiologically and psychologically to ponder about the future, of how to face this type of hurdles. However, it won’t be feasible to evaluate the physical, social and economic effects of this global catastrophe Hence, by comprehending the past, the present and the emerging technologies for the future, this paper made an attempt to outline the clinical implications, treatment approaches like medicines, nutrients and lifestyle management and potential future therapeutic interventions for the control of century’s advancing pandemic.
Cancer is one of the leading causes of death across the world, which is caused by tumours. Breast Cancer (BC) is the most common cancer in women and the second most common cancer death in women. A variety of molecular biomarkers are being used to predict BC susceptibility, including hormone receptors for subtyping and several genes involved in genome maintenance. Hence, biomarkers have specific importance in translational and clinical development to improve diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment since they have advantages in detection time and energy efficiency. The impact of breast cancer, as well as BC risk factors, identification of high-risk groups, screening modalities, and guidelines for screening average-risk and high-risk individuals, therapy advancement using various types of biomarkers. This review describes the design, approval, and distribution of biomarkers and outlines the many types of biomarkers currently used in breast cancer.
ABSTRACT
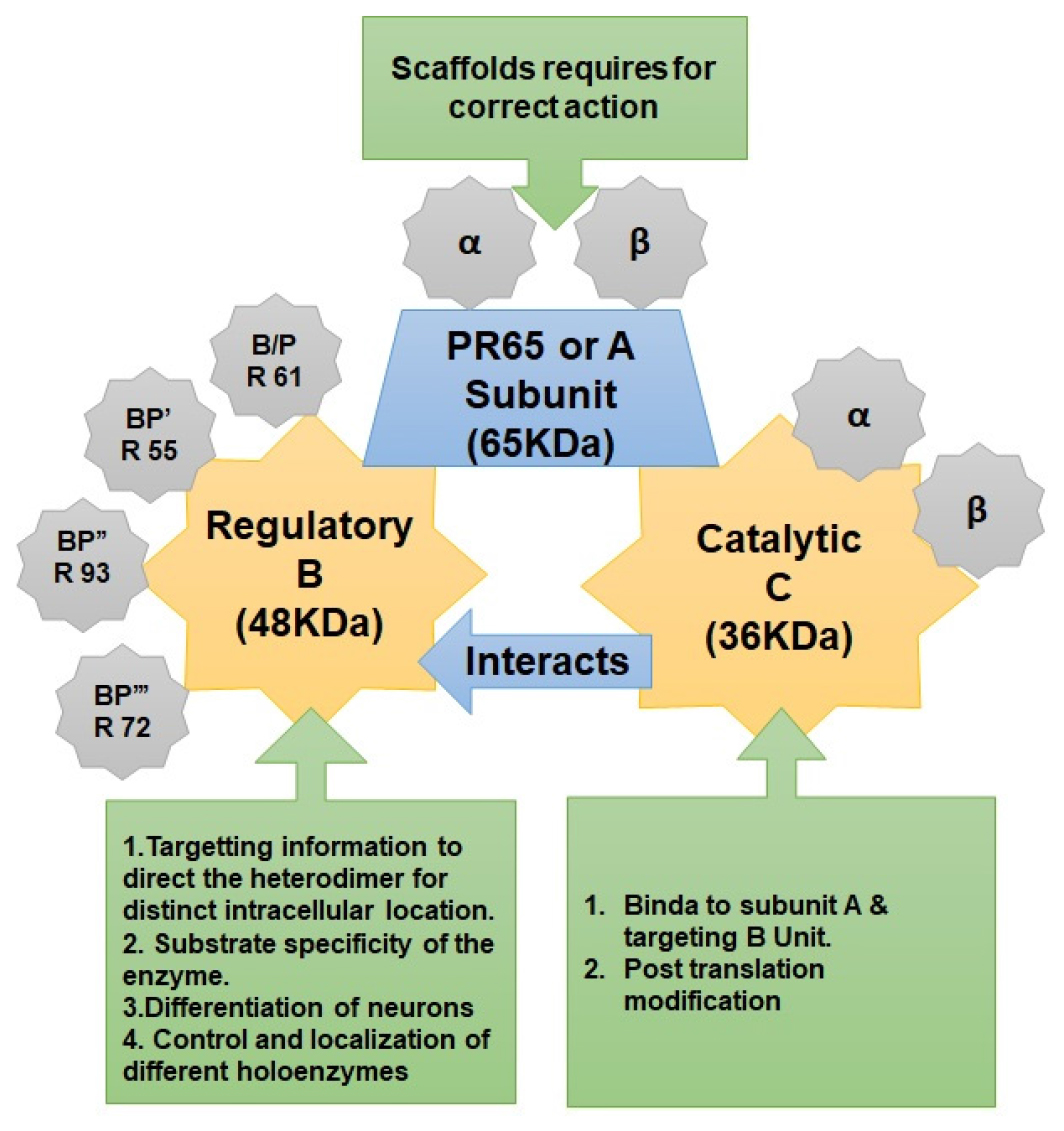
Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive brain condition. It is characterized by alterations in the brain that result in the deposition of certain proteins. The brain shrinks and finally dies as a result of Alzheimer’s disease. Over the years there has been very concerned efforts to control Alzheimer’s disease with strategies like vaccinations but all off them failed in phase three trial. This leads to exploration of new strategy like activation of Protein Phosphatase 2A (PP2A) to control the tau phosphorylation in Alzheimer’s. In this review, a comprehensive review regarding activation of PP2A using drugs like metformin, sphingosides, ceramides, folate and xylulose 5 phosphate, Sodium selenate, Adamantane derivatives, phenolic derivatives, Isoquinolones and Tetralones. Therefore, this approach can offer a fresh glimmer of hope for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease.

ABSTRACT
A new class of biopharmaceuticals are developed by changing profile in terms of chemistry structure and functionality resulting in enhanced efficacy in terms of reduction in immunogenicity toxicity and improvement in half-life and pharmacodynamic activity. The term “BioBetter” refers to a form of biologic that has been enhanced for safety, and patient compliance while lowering the overall cost of healthcare. Despite the fact that BioBetters generally have advantages, they will still face a number of challenges, including high costs for clinical trials, regulatory approval, patent disputes, and market opportunities. Therefore, the development of BioBetter necessitates striking a careful balance between improving patient medical management without sacrificing innovation for corporate success. Two approaches are followed to develop BioBetters Changes in formulation and engineering the protein molecule. In this article we provided a brief overview of a better development like recombinant fusion, antibody engineering and PEGylation.

Diabetes type 3C is referred to as pancreatogenic diabetes also, which is occurring due to pancreatic cancer, pancreatitis, cystic fibrosis, and also pancreatic disease. In this condition, there is an inconsistent blow from hypoglycemia to hyperglycemia, which occurs due to metabolic abnormalities due to tissue damage in the pancreas. Henceforth, the diagnosis and management of this rare condition is a challenging task for healthcare providers. A group from Germany named Ewald and colleagues has observed that among diabetes patients, 8% of patients suffer from T3cDM having chronic pancreatitis, and the occurrence range varies from 5-8%. Type 3cDM incidence is more in patients with surgical resection, especially in the distal pancreas, the presence of pancreatic calcifications and they are on the verge of developing DM in chronic pancreatitis. Pancreatogenous DM is defined as the development of diabetes mellitus in patients due to exocrine pancreas disease, according to recent literature it’s been referred to as type c diabetes. Due to heterogeneity, DM is presently comprised of four types. (1 to 4), depending upon the consumption of tobacco, and often it’s linked with alcohol-abusing which is considered to be a predisposition factor in the disorders related to the pancreas. Diabetes type 3C is referred to as pancreatogenic diabetes also, which is occurring due to pancreatic cancer, pancreatitis, cystic fibrosis, and also pancreatic disease. In this condition, there is an inconsistent blow from hypoglycemia to hyperglycemia, which occurs due to metabolic abnormalities due to tissue damage in the pancreas. Henceforth, the diagnosis and management of this rare condition is a challenging task for healthcare providers.

The majority of millet is grown in Nigeria, Mali, Faso, Burkina, Chad, China and India. There are many different types of millet found throughout the universe, but finger millet, small millet, foxtail millet, and proso millet are the most prevalent millets. Among the tiny millets, finger millet (Eleusine coracana (L.) Gaertn) has the most area under cultivation in India. Finger millet is the only minor cereal with better nutritional value than barley, rye, and oats, and it has exceptional features as a livelihood food product. It is one of the most significant minor millets, with a high calcium content (344 mg/100g), dietary fibre (18%), phytates (0.48%), and phenolics (0.3–3%). Other than that, it contains significant amounts of iron (3.9 mg), riboflavin (0.19 mg), thiamine (0.42 mg), and amino acids including isoleucine, phenylalanine, leucine, and methionine. Due to its nutraceutical potential, these phytochemicals make finger millet a powerhouse of health-promoting nutrients. It has anti-diabetic, anti-microbial, anti-cancer, antioxidant, anti-aging, anti-bacterial, and hepatoprotective characteristics along with other health benefits. We are exploring the potential of Eleusinecoracana through this review.
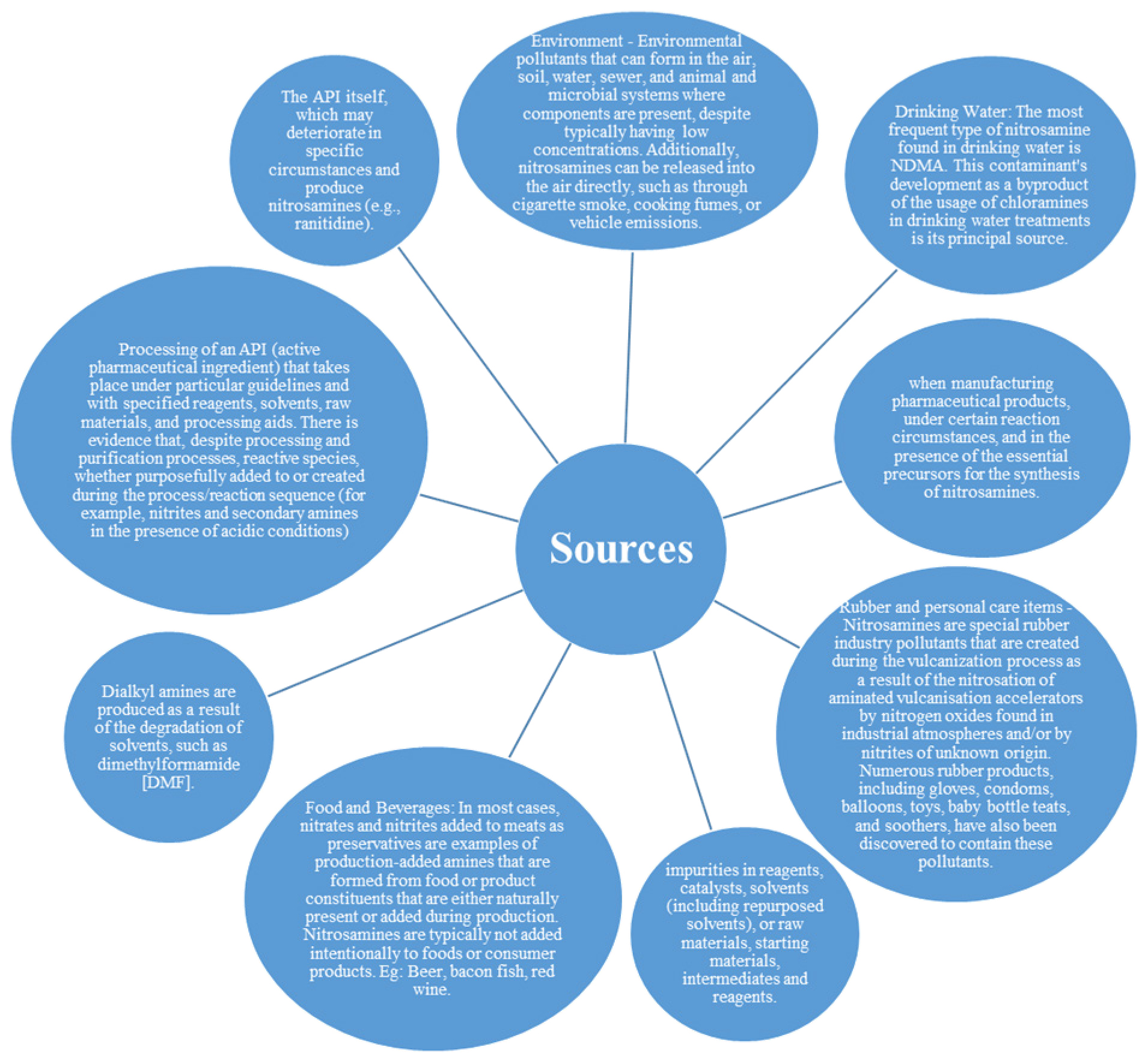
ABSTRACT
The seriousness of presence of nitrosamines came to Limelight after USFDA and EMEA declared in July 2018 that N-Nitroso dimethylamine and N-N-NDMA are focused on the pharmaceutical medicinal products and particularly used in case of SARTANS that are used in the treatment of Hypertension and Angiotensin II receptor blockers. Later the list was expanded to include Histamine-2 blocker Ranitidine and Diabetes drug Pioglitazone. Reaction of Urea Derivatives, Secondary amide carbamates and amines with Nitrogenous agent and nitrates lead to formation of Nitrosamines. The Oxidation state of nitrogen is +3. The Reasons for Presence of Nitrosamines in Pharmaceutical Products can be due to Product Degradation, Catalysts, solvents, Chemical reagents, Cross Contamination, Manufacturing Process and Contamination of Raw Materials. Technologies like Gas Chromatography, Mass Spectroscopy, Light Chromatography Mass spectroscopy are used to detect Nitrosamine Contamination. N-Nitrosamines categorized as “Cohort of concern” in ICH guidelines due to their potential mutagenic and carcinogenic nature. N-Nitroso dimethylamine and N-Nitroso diethylamine are classified as Class 2A human carcinogens by IARC-International Agency for Research and Cancer. This study focused on profile of nitrosamine impurities and regulations governing their presence in drug products.

